Alanya
Alanya, formerly known as Alaiye, is a beach resort city and a district in the Antalya Province of Turkey. It is located on the southern coast of Turkey’s Mediterranean Region, approximately 133 kilometers (83 miles) east of Antalya. The city has a population of around 98,627 people, according to the 2010 census, and the district, including the city and its surrounding area, has a population of 248,286.
Alanya has a rich history and has been a significant stronghold for various Mediterranean empires throughout the centuries, including the Ptolemaic, Seleucid, Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman Empires. The city’s strategic location on a small peninsula into the Mediterranean Sea, surrounded by the Taurus Mountains, has contributed to its historical importance. Many landmarks in Alanya, such as the Kızıl Kule (Red Tower), Tersane (Shipyard), and Alanya Castle, were built during the rule of Alaeddin Kayqubad I, a Seljuk Sultan, in the Middle Ages.
Today, Alanya is a popular tourist destination known for its Mediterranean climate, natural attractions, and historical heritage. It attracts a significant number of tourists, accounting for nine percent of Turkey’s tourism sector and thirty percent of foreign real estate purchases in the country. The tourism industry has boomed since 1958, making it the dominant industry in the city and leading to a growth in its population. Alanya also hosts warm-weather sporting events and cultural festivals on an annual basis.
Names
The city has undergone several name changes throughout history. It was known as Coracesium in Latin and Korakesion in Greek during ancient times. Under the Byzantine Empire, it was called Kalonoros or Kalon Oros, meaning “beautiful mountain” in Greek. The Seljuks renamed the city Alaiye, derived from the name of Sultan Alaeddin Kayqubad I. In the 13th and 14th centuries, Italian traders referred to the city as Candelore or Cardelloro. The modern name “Alanya” was established by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk in 1935.
History

Piri Reis map of Alanya from 1525 showing the extent of the medieval city and the location on the Pamphylia plain.
Finds in the nearby Karain Cave indicate occupation during the Paleolithic era as far back as 20,000 BC, and archeological evidence shows a port existed at Syedra, south of the modern city, during the Bronze Age around 3,000 BC. A Phoenician language tablet found in the district dates to 625 BC, and the city is specifically mentioned in the 4th-century BC Greek geography manuscript, the periplus of Pseudo-Scylax. The castle rock was likely inhabited under the Hittites and the Achaemenid Empire, and was first fortified in the Hellenistic period following the area’s conquest by Alexander the Great. Alexander’s successors left the area to one of the competing Macedonian generals, Ptolemy I Soter, after Alexander’s death in 323 BC. His dynasty maintained loose control over the mainly Isaurian population, and the port became a popular refuge for Mediterranean pirates. The city resisted Antiochus III the Great of the neighboring Seleucid kingdom in 199 BC, but was loyal to the pirate Diodotus Tryphon when he seized the Seleucid crown from 142 to 138 BC. His rival Antiochus VII Sidetes completed work in 137 BC on a new castle and port, begun under Diodotus.
The Roman Republic fought Cilician pirates in 102 BC, when Marcus Antonius the Orator established a proconsulship in nearby Side, and in 78 BC under Servilius Vatia, who moved to control the Isaurian tribes. The period of piracy in Alanya finally ended after the city’s incorporation into the Pamphylia province by Pompey in 67 BC, with the Battle of Korakesion fought in the city’s harbor. In Strabo’s reckoning, Coracesium marked the boundary between ancient Pamphylia and Cilicia (Cilicia Trachaea, in particular); though other ancient authors placed the boundary elsewhere. Isaurian banditry remained an issue under the Romans, and the tribes revolted in the fourth and fifth centuries AD, with the largest rebellion being from 404 to 408.
With the spread of Christianity Coracesium, as it was called, became a bishopric. Its bishop Theodulus took part in the First Council of Constantinople in 381, Matidianus in the Council of Ephesus in 431, Obrimus in the Council of Chalcedon in 451, and Nicephorus (Nicetas) in the Third Council of Constantinople in 680. Coracesium was a suffragan of the metropolitan see of Side, the capital of the Roman province of Pamphylia Prima, to which Coracesium belonged. It continued to be mentioned in the Notitiae Episcopatuum as late as the 12th or 13th century. No longer a residential bishopric, Coracesium is today listed by the Catholic Church as a titular see.
Islam arrived in the 7th century with Arab raids, which led to the construction of new fortifications. The area fell from Byzantine control after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071 to tribes of Seljuk Turks, only to be returned in 1120 by John II Komnenos.

Statue of Kayqubad I in Alanya
Following the Fourth Crusade’s attack on the Byzantines, the Christian Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia periodically held the port, and it was from an Armenian, Kir Fard, that the Turks took lasting control in 1221 when the Anatolian Seljuk Sultan Alaeddin Kayqubad I captured it, assigning the former ruler, whose daughter he married, to the governance of the city of Akşehir. Seljuk rule saw the golden age of the city, and it can be considered the winter capital of their empire. Building projects, including the twin citadel, city walls, arsenal, and Kızıl Kule, made it an important seaport for western Mediterranean trade, particularly with Ayyubid Egypt and the Italian city-states. Alaeddin Kayqubad I also constructed numerous gardens and pavilions outside the walls, and many of his works can still be found in the city. These were likely financed by his own treasury and by the local emirs, and constructed by the contractor Abu ‘Ali al-Kattani al-Halabi. Alaeddin Kayqubad I’s son, Sultan Gıyaseddin Keyhüsrev II, continued the building campaign with a new cistern in 1240.
At the Battle of Köse Dağ in 1243, the Mongol hordes broke the Seljuk hegemony in Anatolia. Alanya was then subject to a series of invasions from Anatolian beyliks. Lusignans from Cyprus briefly overturned the then ruling Hamidid dynasty in 1371. The Karamanids sold the city in 1427 for 5,000 gold coins to the Mamluks of Egypt for a period before General Gedik Ahmed Pasha in 1471 incorporated it into the growing Ottoman Empire. The city was made a capital of a local sanjak in the eyalet of Içel. The Ottomans extended their rule in 1477 when they brought the main shipping trade, lumber, then mostly done by Venetians, under the government monopoly. On September 6, 1608, the city rebuffed a naval attack by the Order of Saint Stephen from the Duchy of Florence.

The Seljuk era Tersane was a drydock for ships.
Trade in the region was negatively impacted by the development of an oceanic route from Europe around Africa to India, and in the tax registers of the late sixteenth century, Alanya failed to qualify as an urban center. In 1571 the Ottomans designated the city as part of the newly conquered province of Cyprus. The conquest further diminished the economic importance of Alanya’s port. Traveler Evliya Çelebi visited the city in 1671/1672, and wrote on the preservation of Alanya Castle, but also on the dilapidation of Alanya’s suburbs. The city was reassigned in 1864 under Konya, and in 1868 under Antalya, as it is today. During the 18th and 19th centuries numerous villas were built in the city by Ottoman nobility, and civil construction continued under the local dynastic Karamanid authorities. Bandits again became common across Antalya Province in the mid-nineteenth century.
After World War I, Alanya was nominally partitioned in the 1917 Agreement of St.-Jean-de-Maurienne to Italy, before returning to the Turkish Republic in 1923 under the Treaty of Lausanne. Like others in this region, the city suffered heavily following the war and the population exchanges that heralded the Turkish Republic, when many of the city’s Christians resettled in Nea Ionia, outside Athens. The Ottoman census of 1893 listed the number of Greeks in the city at 964 out of a total population of 37,914. Tourism in the region started among Turks who came to Alanya in the 1960s for the alleged healing properties of Damlataş Cave, and later the access provided by Antalya Airport in 1998 allowed the town to grow into an international resort. Strong population growth through the 1990s was a result of immigration to the city, and has driven a rapid modernization of the infrastructure.
Geography
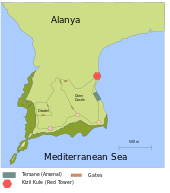
Map of the Alanya Peninsula
Geographically, Alanya is situated on the Gulf of Antalya, surrounded by the Taurus Mountains to the north and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It occupies approximately 70 kilometers (43 miles) of coastline and is part of the Turkish Riviera. The city is bordered by the Manavgat district along the coast, the Gündoğmuş mountains inland, and other districts in the provinces of Konya and Karaman.
The Pamphylia plain between the sea and the mountains is an isolated example of an Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forest, which include Lebanon Cedar, evergreen scrub, fig trees, and black pine. The Alanya Massif refers to the area of metamorphic rocks east of Antalya. This formation is divided into three nappes from lowest to highest, the Mahmutlar, the Sugözü, and the Yumrudağ. The similar lithology extends beneath the city in a tectonic window. Bauxite, an aluminum ore, is common to the area north of city, and can be mined.

Tip of the Alanya Peninsula
The town is divided east–west by a rocky peninsula, which is the distinctive feature of the city. The harbor, city center, and Keykubat Beach, named after the Sultan Kayqubad I, are on the east side of the peninsula. Damlataş Beach, named for the famous “dripping caves”, and Kleopatra Beach are to the west. The name “Cleopatra” possibly derives from either the Ptolemaic princess’ visit here or the area’s inclusion in her dowry to Mark Antony. Atatürk Bulvarı, the main boulevard, runs parallel to the sea, and divides the southern, much more touristic side of Alanya from the northern, more indigenous side that extends north into the mountains. Ring Road Street, another major road, encircles the main town to the north.
Climate
Alanya has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, with long, hot, and dry summers and mild, wet winters. The presence of the Taurus Mountains causes fog, creating visible rainbows on many mornings. The sea temperature in Alanya averages 21.4°C (71°F) annually, with August being the warmest month.
Alanya offers a combination of natural beauty, historical sites, and a vibrant tourism industry, making it a popular destination for visitors from around the world.